|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The Polygon Ecosystem Token (POL) is the latest native token within the Polygon ecosystem. This new token has been designed to become an integral part of the core functions of major Polygon products and applications. POL is intended to eventually take over the roles of the MATIC token in terms of governance, transaction fees, and other utilities within the growing Polygon ecosystem.
According to Polygon, POL represents a technical and economic upgrade compared to MATIC. It has been built to be adaptable to the evolving ecosystem, ensuring scalability and enhanced security. This adaptability allows validators to secure multiple chains, providing support for the Polygon ecosystem’s growth.
Initially, there will be 10 billion POL tokens dedicated to the migration from MATIC to POL. In the future, these tokens will be emitted as rewards for validators at a predetermined rate, which cannot exceed 1%. However, this rate can be adjusted through governance after 10 years when the Polygon ecosystem matures.
So, let’s dive into the key roles POL will play in this expanding ecosystem.
Utility of the POL Token:
Polygon describes POL as a highly versatile token that offers numerous benefits to its holders. It serves as the native currency for the Polygon ecosystem, functioning as the primary token for transactions and fees on the network.
In addition to this, POL will contribute to the security, economy, and management of the Polygon ecosystem through a process called “Restaking.” This is a concept where token holders can stake their POL to secure the network and earn rewards for their efforts. Validators who stake a specified amount of POL tokens can become part of the network’s validator nodes, ensuring network security. This system also allows for validators to earn rewards from transaction fees on secondary networks they validate.
Moreover, POL tokens grant holders governance rights. This means that every token holder has the opportunity to participate in community decision-making processes. Although the full details of the governance system are yet to be published, it is expected to operate in a manner similar to most decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). This means that token holders can vote on various project proposals, whether they pertain to technology, administration, or finance.
Polygon 2.0: Powered by ZK Technology:
On June 20, 2023, the Polygon Labs team proposed a significant transformation of the Polygon Proof of Stake (PoS) chain into a full zkEVM validium network. This move aims to enhance the security of the network by adopting zkEVM technology, aligning Polygon with Ethereum’s higher security standards. It also addresses consensus issues and fluctuations in gas estimation efficiency to provide users with an improved experience.
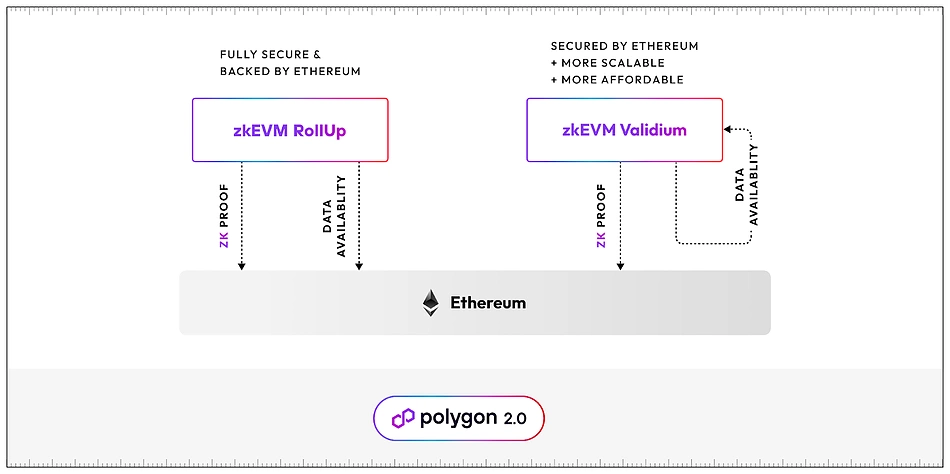
What Are zkEVM Validiums?
ZkEVM validiums offer an alternative to rollups for implementing zk-powered Layer 2 solutions. These systems submit validity proofs to Ethereum, ensuring secure transactions. Unlike rollups, which publish transaction data to Ethereum, validiums guarantee data availability through an alternative method. This approach reduces fees and improves scalability.
Polygon 2.0 Supernet Structure:
Polygon aims to create an efficient value layer through decentralized technologies in the upgrade. This upgrade transforms Polygon into a supernet of ZK networks, operating as an interoperable system. It establishes a uniform security system and near-instant transaction finality using ZK provers.
Features of Polygon 2.0:
- The Staking layer utilizes a proof of stake consensus algorithm and manages validator staking and management.
- The Interop layer is responsible for intercommunication between networks within the supernet.
- The Execution layer, where transactions are screened and validated.
- The Proving layer generates proofs for executed transactions.
Polygon CDK:
To simplify the development of zero-knowledge Layer 2 networks, Polygon introduces the Chain Development Kit (CDK). This open-source framework allows developers to launch networks on the supernet, inheriting the security and decentralization features of Polygon 2.0.
What Happens to the MATIC Token?
The MATIC token will be phased out and replaced by POL. MATIC holders will need to swap their tokens at a 1:1 ratio to POL through an upgrade smart contract. This phase-out process will take over four years to allow ample time for token migration.
Final Thoughts:
Polygon’s shift towards ZK and Layer 2 technologies is a significant development, offering the potential to reshape the landscape for decentralized applications and smart contract projects within the ecosystem. However, it’s essential to stay informed about these changes and exercise caution, as new systems can be technically volatile. Remember to conduct your research before investing in any tokens or protocols.
Crypto and blockchain enthusiast.




